Überwachung einer Rundstrickmaschine mittels Sensorik: Abschluss des Projektes mit der thoenes® Dichtungstechnik GmbH
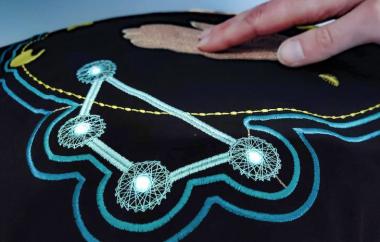
Betriebsdaten sinnvoll nutzen und Ausfallzeiten reduzieren: Das waren nur einige der Ziele, die die Textil vernetzt-Kollegen vom Sächsischen Textilforschungsinstitut (STFI) beim Retrofitting einer Rundstrickmaschine bei der thoenes® Dichtungstechnik GmbH aus dem sächsischen Klipphausen erreicht haben.
Die Rundstrickmaschine produziert Kunststoffgestricke, die unter anderem im Fahrzeugbau zum Einsatz kommen, um Druckluftgeräusche zu reduzieren. Die derzeit erhobenen Daten werden in Ermangelung an Schnittstellen momentan noch nicht an übergeordnete Systeme übergeben und weiterverarbeitet. Das Team vom STFI hat nun eine sensorbasierte Nachrüstung der Maschine vorgenommen. Dazu haben sich die Kollegen in mehreren Workshops einen Überblick verschafft, welche Anforderungen in der laufenden Produktion anfallen. Im Mittelpunkt standen die Messung der Drehzahl und die Bestimmung des Spulendurchmessers, um Laufzeit, Geschwindigkeit und Verarbeitungsmenge an der Maschine zu erfassen. Hierzu verbaute thoenes einen Hallsensor an der Maschine, der zur Drehzahlmessung genutzt wurde. Am STFI wurden zudem weitere Erfassungsmethoden erprobt. Die Programmierung der Controller-Systeme erfolgte in der Programmiersprache C und für die Vorauswertung der Sensordaten kam das grafische Programmierwerkzeug Node-RED zum Einsatz. Dieses nutzt das Unternehmen zudem, um mobil Störungsmeldungen zu erfassen.
Am Chemnitzer Schaufenster des STFI ist nun die Realisierung eines Retrofit-Demonstrators geplant. Hieran sollen weitere Lösungsansätze gezeigt werden, zugleich wird dieser anderen interessierten Unternehmen als Leihgabe zur Verfügung stehen.
Mittelstand 4.0-Kompetenzzentrum Textil vernetzt