ITA: Forschungsprojekte zu biobasierten Textilien
Wissenschaftsteams des Instituts für Textiltechnik der RWTH Aachen University (ITA) forschen gemeinsam mit Partnern aus der Industrie und außeruniversitären Forschungseinrichtungen gefördert vom Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF) an Wegen, die Textilindustrie von fossilen auf biobasierte Rohstoffe, Ausrüstungen sowie neue umweltfreundliche Verfahren umzustellen, um auf diese Weise, die gesamte textile Wertschöpfungskette zu transformieren.
Die Fäden dafür laufen im Innovationsraum BIOTEXFUTURE mit einer Vielzahl an einzelnen Textilforschungsprojekten zusammen. Die enge Verknüpfung von universitärer mit anwendungsnaher Forschung und marktrelevanter Umsetzung mit Wirtschaftsunternehmen soll dazu führen, dass der Textilindustrie die Wende zu einem zukunftsfähigen biobasierten Wirtschaften zielgerichtet gelingen kann.
Erste konkrete Ergebnisse ausgewählter Projekte präsentiert BIOTEXFUTURE auf den Gemeinschaftsstand Bioökonomie des BMBF auf der Hannover Messe (22. bis 26.4.2024) sowie auf der fast zeitgleich stattfindenden Internationalen Leitmesse für technische Textilien und Vliesstoffe, Techtextil, in Frankfurt / Main (23. bis 26.4.2024). Folgende Projekte werden vorgestellt:
- BioTurf: der Kunstrasen der Zukunft ist grün (Hannover Messe / Techtextil)
- CO2Tex: innovative elastische Garne binden CO2 (Hannover Messe / Techtextil)
- DegraTex: biologisch abbaubare Geotextilien (Techtextil)
- BioBase: Textilien für Innenräume, Sport, Auto und Technik werden bio (Hannover Messe / Techtextil)
BioTurf: der Kunstrasen der Zukunft ist grün
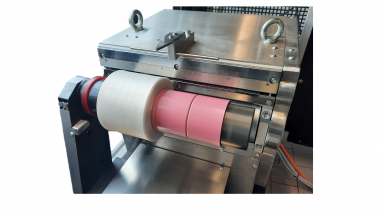
Die Forscher*innen des Projekts BioTurf arbeiten an der Lösung eines Problems, mit dem hunderte von Städten und Gemeinden konfrontiert sind. Ziel ist es, eine Kunstrasenstruktur aus Bio-Polyethylen (PE) zu entwickeln, das sich qualitativ nicht von erdölbasiertem PE unterscheidet. Diese Monomaterial-Struktur soll ein hochwertiges Materialrecycling ermöglichen. Eine wichtige Basis für die spätere Kreislaufführung des Produktes. Darüber hinaus wird die neuartige Kunstrasenstruktur ohne die Zugabe von Einstreu-Granulat auskommen und damit das aktuelle Mikroplastik-Problem von Kunstrasenplätzen lösen. Es existiert bereits ein BioTurf-Fußballplatz in Aachen als Demonstrationsspielfeld, auf denen Sportler*innen spielen und trainieren, und dadurch die Forscher*innen regelmäßig Rückmeldung bekommen. Man befindet sich in der Phase der Feinjustierung, um das Ziel zu erreichen den Kunstrasen der Zukunft aus 100% biobasiertem Polyethylen herstellen zu können.
CO2Tex: innovative elastische Garne binden CO2
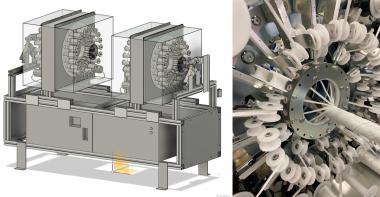
Die Textilwissenschaftler*innen des BIOTEXFUTURE Projekts CO2Tex entwickeln elastische Filament-Garne, in deren Ausgangsmaterial das für die Erderwärmung mitverantwortliche Treibhausgas CO2 gebunden ist. Gleichzeitig verwenden sie für die Garnherstellung Schmelzspinnprozesse, für die keine giftigen und umweltschädlichen Lösungsmittel notwendig sind. Den Forscher*innen ist es zudem gelungen, die Elastizität der auf thermoplastischen Polyurethanen (TPU) beruhenden Entwicklung für bestimmte Garntypen an das Leistungsvermögen der konventionellen Elastane heranzuschrauben. Das Projekt-Konsortium erwartet, dass für die entwickelten CO2-haltigen elastischen TPU-Filament-Garne eine Hochskalierung der Produktionsprozesse auf eine massentaugliche Fertigung im Industriemaßstab in absehbarer Zeit möglich sein wird. Dabei hält das CO2Tex-Team vergleichbare Herstellungskosten wie bei konventionellen Garnen sowie leichte Vorteile bei der Energiebilanz gegenüber bestehenden Prozessen für möglich.
DegraTex: biologisch abbaubare Geotextilien
Das Ziel von DegraTex ist die Entwicklung biobasierter, abbaubarer Geotextilien für kurzfristige Anwendungen wie die zeitlich begrenzte Sicherung von Erdstrukturen oder für den Vegetationsschutz. Die Materialien erfüllen ihre Funktion, bis sie von natürlichen Komponenten, wie z.B. bodenstabilisierenden oder bodendeckenden Pflanzen, übernommen werden oder simpel einfach nicht mehr benötigt werden. Es geht darum, konventionelle, erdölbasierte Geotextilien in technisch und ökologisch sinnvollem Rahmen durch biobasierte und abbaubare Produktlösungen zu ersetzen. Das Forschungsteam des ITA hat bereits erste Demonstratoren auf Basis von Biopolymeren im Außeneinsatz.
BioBase: Textilien für Innenräume, Sport, Auto und Technik werden bio
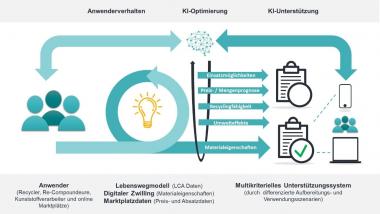
Im BioBase-Projekt wird die gesamte textile Wertschöpfungskette der jeweiligen Produkte abgebildet und in jedem Prozessschritt der technologische Reifegrad für die industrielle Produktion von biobasierten und nachhaltigen Chemiefasern schrittweise erhöht. Zunächst entstehen hierbei in Kooperation zwischen den Forschungseinrichtungen und Industriepartner*innen industriell gefertigte Anschauungsmodelle (Demonstratoren), die das Potenzial der am Markt verfügbaren biobasierten Polymere demonstrieren sollen. Die Herstellung der Polymere, Garne und textilen Flächen, orientiert sich sehr anwendungsbezogen an den existierenden technischen Anforderungen in den unterschiedlichen Industrie-Sektoren.
Das Team in Aachen beschäftigt sich mit der Herstellung von Chemiefasergarnen und betrachtet dabei die Arbeitsschritte Schmelzspinnen und Texturieren der Wertschöpfungskette und teilweise auch die Flächenherstellung. Die Forschungen zeigen, dass biobasierte Polymere existieren, die auf bestehenden Anlagen entlang der textilen Prozesskette bis zum Demonstrator verarbeitbar sind, wobei die Garn- und Textileigenschaften je nach Anforderungsprofil angepasst werden können.
ITA – Institut für Textiltechnik der RWTH Aachen University