Embroidery as Low-Cost Solution for Making Wearable Electronics
Embroidering power-generating yarns onto fabric allowed researchers to embed a self-powered, numerical touch-pad and movement sensors into clothing. The technique offers a low-cost, scalable potential method for making wearable devices.
“Our technique uses embroidery, which is pretty simple – you can stitch our yarns directly on the fabric,” said the study’s lead author Rong Yin, assistant professor of textile engineering, chemistry and science at North Carolina State University. “During fabric production, you don’t need to consider anything about the wearable devices. You can integrate the power-generating yarns after the clothing item has been made.”
In the study published in Nano Energy, researchers tested multiple designs for power-generating yarns. To make them durable enough to withstand the tension and bending of the embroidery stitching process, they ultimately used five commercially available copper wires, which had a thin polyurethane coating, together. Then, they stitched them onto cotton fabric with another material called PTFE.
“This is a low-cost method for making wearable electronics using commercially available products,” Yin said. “The electrical properties of our prototypes were comparable to other designs that relied on the same power generation mechanism.”
The researchers relied on a method of generating electricity called the “triboelectric effect,” which involves harnessing electrons exchanged by two different materials, like static electricity. They found the PTFE fabric had the best performance in terms of voltage and current when in contact with the polyurethane-coated copper wires, as compared to other types of fabric that they tested, including cotton and silk. They also tested coating the embroidery samples in plasma to increase the effect.
“In our design, you have two layers – one is your conductive, polyurethane-coated copper wires, and the other is PTFE, and they have a gap between them,” Yin said. “When the two non-conductive materials come into contact with each other, one material will lose some electrons, and some will get some electrons. When you link them together, there will be a current.”
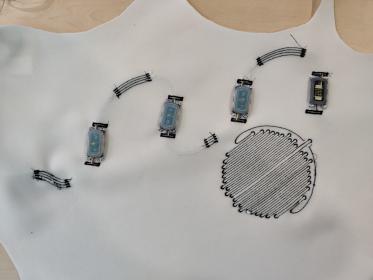
Researchers tested their yarns as motion sensors by embroidering them with the PTFE fabric on denim. They placed the embroidery patches on the palm, under the arm, at the elbow and at the knee to track electrical signals generated as a person moves. They also attached fabric with their embroidery on the insole of a shoe to test its use as a pedometer, finding their electrical signals varied depending on whether the person was walking, running or jumping.
Lastly, they tested their yarns in a textile-based numeric keypad on the arm, which they made by embroidering numbers on a piece of cotton fabric, and attaching them to a piece of PTFE fabric. Depending on the number that the person pushed on the keypad, they saw different electrical signals generated for each number.
“You can embroider our yarns onto clothes, and when you move, it generates an electrical signal, and those signals can be used as a sensor,” Yin said. “When we put the embroidery in a shoe, if you are running, it generates a higher voltage than if you were just walking. When we stitched numbers onto fabric, and press them, it generates a different voltage for each number. It could be used as an interface.”
Since textile products will inevitably be washed, they tested the durability of their embroidery design in a series of washing and rubbing tests. After hand washing and rinsing the embroidery with detergent, and drying it in an oven, they found no difference or a slight increase in voltage. For the prototype coated in plasma, they found weakened but still superior performance compared with the original sample. After an abrasion test, they found that there was no significant change in electrical output performance of their designs after 10,000 rubbing cycles.
In future work, they plan to integrate their sensors with other devices to add more functions.
“The next step is to integrate these sensors into a wearable system,” Yin said.
The study, “Flexible, durable and washable triboelectric yarn and embroidery for self-powered sensing and human-machine interaction,” was published online in Nano Energy. Co-authors included Yu Chen, Erdong Chen, Zihao Wang, Yali Ling, Rosie Fisher, Mengjiao Li, Jacob Hart, Weilei Mu, Wei Gao, Xiaoming Tao and Bao Yang. Funding was provided by North Carolina State University through the NC State Faculty Research & Professional Development Fund and the NC State Summer REU program.
North Carolina State University, Rong Yin, Laura Oleniacz