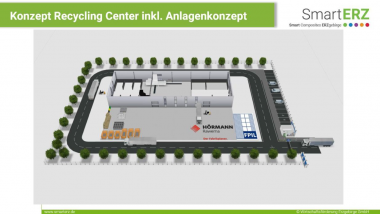
Forschungsvorhaben "Nachhaltigkeit im Bereich der Textilbranche"
An der Technischen Universität Chemnitz wird ein Forschungsvorhaben zum Thema "Nachhaltigkeit im Bereich der Textilbranche" durchgeführt. Für die dazugehörigen Umfrage werden Textilunternehmen gesucht, die sich daran beteiligen möchten.
Das Management von Nachhaltigkeit und die entsprechende Berichtpflicht betrifft die gesamte Textilwirtschaft. Aus wissenschaftlicher Sicht fehle, so die Verantwortlichen, jedoch über die Textilbranche, insbesondere über die Bekleidungsindustrie hinaus, noch Wissen zum Thema Nachhaltigkeit. Mit Hilfe der Umfrage soll festgehalten werden, in welchem Umfang Textilunternehmer:in die Themen Nachhaltigkeit und Ökobilanzierung bereits berücksichtigen.
Die Umfrage hat eine geschätzte Bearbeitungsdauer von 15 Minuten und ist unter folgendem Link aufrufbar. Datenschutzrechtlich sind die Angaben anonymisiert, ein Rückschluss auf Unternehmen oder Personen ist nicht möglich.
Professur Fabrikplanung und Intralogistik
Fakultät für Maschinenbau
Technische Universität Chemnitz