Oerlikon Barmag celebrates its 100th anniversary
- Innovation begins with creativity
- A pioneer of the manmade fiber industry
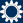
When the manmade fiber age began a century ago, a German company was responsible for the pioneering work involved. Barmag, established in 1922, was one of the world’s first companies to construct machines for the large-scale production of synthetic staple fibers. To this day, the leading manufacturer of manmade fiber spinning systems and texturing machines in Remscheid – a brand under the aegis of the Swiss Oerlikon Group since 2007 – has shaped technological progress in this sector; in future, with ever more innovations focusing on sustainability and digitalization.
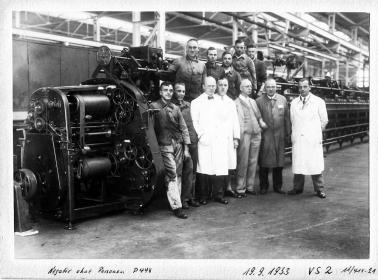
Barmer Maschinenfabrik Aktiengesellschaft (Barmag) is founded in Barmen, located in the Bergische Land region, on March 27, 1922. The German and Dutch founders enter unchartered technological territory, one created as the result of a groundbreaking invention: in 1884, French chemist Count Hilaire Bernigaud de Chardonnet used nitrocellulose to produce the first so-called artificial silk, later known as rayon. The following decades see rapid development focusing on the search for synthetic textile fibers and their manufacturing technologies. As one of the first machine factories, Barmag battles its way through the eventful early years of the manmade fiber industry, the ‘Roaring Twenties’ and the Great Depression – and suffers the extensive destruction of its factories at the end of World War Two. Rebuilding is successful. With the unstoppable success story of purely synthetic plastic fibers such as polyamide, the company flourishes from the 1950s through to the 1970s, establishing sites in all international, for the textile industry at the time important, industrial regions and garnering prestige across the globe in the process. In the ups and downs of expansion, global competition and crises, Barmag reaches the very pinnacle of the market and becomes the preferred technological development partner for the manmade fiber industries in China, India and Turkey. The company has been a high-impact brand under the umbrella of the Oerlikon Group since 2007.
On the wings of innovation
Today, Oerlikon Barmag is a leading supplier of manmade fiber filament spinning systems and part of the Manmade Fibers Solutions business unit of the Oerlikon Polymer Processing Solutions Division. And our aspirations have not diminished: “The striving towards innovation and technological leadership has been, is and will always be part of our DNA”, emphasizes Georg Stausberg, CEO of Oerlikon Polymer Processing Solutions. In the past, this has been observable in such trailblazing innovations as the revolutionary WINGS generation of winders for POY in 2007 and WINGS for FDY in 2012. Currently, the focus of new and further developments is very much on digitalization and sustainability. Here, Oerlikon Barmag has – as one of the world’s first systems manufacturers – been implementing fully-networked smart factories for globally-leading polyester manufacturers since the end of the last decade. Within this context, digital solutions and automation are also helping to provide greater climate and environmental compatibility. This sustainability commitment is not only evidenced by the e-save label introduced for all products back in 2004: Oerlikon is endeavoring to also make all its sites carbon-neutral by 2030 and to acquire its energy exclusively from renewable sources. An ambitious target, whose achievement could be helped by the Oerlikon Barmag anniversary, states Georg Stausberg: “Innovation begins with creativity. And remembering the past provides plenty of motivation and inspiration for the future.”
 (c) Oerlikon Barmag
(c) Oerlikon Barmag
 (c) Oerlikon Barmag
(c) Oerlikon Barmag
 (c) Oerlikon Barmag
(c) Oerlikon Barmag
 (c) Oerlikon Barmag
(c) Oerlikon Barmag
 (c) Oerlikon Barmag
(c) Oerlikon Barmag
 (c) Oerlikon Barmag
(c) Oerlikon Barmag
 (c) Oerlikon Barmag
(c) Oerlikon Barmag
Oerlikon Barmag Jubiläum Fibers synthetic fibers and yarns Manmade Fibers Solutions Polymer Processing Solutions Georg Stausberg
Oerlikon Barmag