AkzoNobel participates in research program with SusInkCoat project
More than 82 companies, businesses and social organizations – including AkzoNobel – are involved in a major Dutch research program focused on developing new technologies that will help solve some of today’s societal challenges.
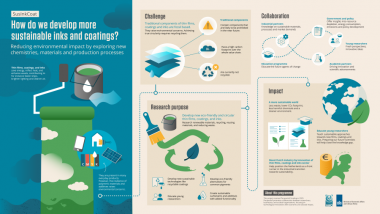
Seven broad consortia have been established as part of the government-funded “Perspectief” program, with AkzoNobel set to play a leading role in the SusInkCoat project, which will explore how to make inks and coatings more sustainable.
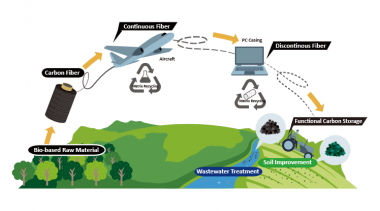
The company will work together with private partners and other societal stakeholders to develop new materials, processes and applications to improve the durability, functionality and recyclability of coatings, thin films and inks. The program, which will run for the next five years, is backed by the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate Policy and the Dutch Research Council (NWO).
“Our discussions about collaborating with our SusInkCoat partners have been very positive,” says AkzoNobel’s R&D Director of Scientific Academic Programs, André van Linden, who is also the co-lead of SusInkCoat. “We’re all facing the same societal challenges – how to become more circular – and we’re looking for the same solutions in different application areas. But we’ve never done that together for this specific research topic, so we need an ecosystem to help us solve these challenges.
Van Linden adds that the program – one of many R&D projects the company is involved with – will also support AkzoNobel’s ambition to achieve 50% less carbon emissions in its own operations – and across the value chain – by 2030.
“We want to make the recyclability of materials - such as furniture, building materials and steel constructions - easier by introducing functionalities like self-healing, higher durability and triggered release,” he continues. “The more you can leave the materials in their original state, the more sustainably you can operate.”
AkzoNobel will be collaborating with Canon, Evonik, GFB, PTG and RUG Ventures, who together possess extensive knowledge of market demands, supply chains and production processes. All the SusInkCoat partners will also work with academic researchers at several Dutch universities in an effort to identify promising developments that can be commercialized, used for education purposes or for outreach to the public.
Research being conducted by the other six consortia includes investigating methods to make tastier plant-based food; flat optics for more sustainable hi-tech equipment; and cheaper and more accessible medical imaging technology.
AkzoNobel