European composites market on the level of 2014
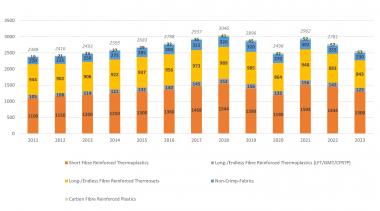
After a long phase of continuous growth, the composites market has seen strong fluctuations since 2018. In 2023, the overall market for composites in Europe fell by 8%.
The current mood on the markets in Germany and Europe is rather negative within the industry. The main drivers are the persistently high energy and raw material prices. Added to this are problems in logistics chains and a cautious consumer climate. A slowdown in global trade and uncertainties in the political arena are fueling the negative sentiment. Despite rising registration figures, the automotive industry, the most important application area for composites, has not yet returned to its pre-2020 volume. The construction industry, the second key application area, is currently in crisis. These factors have already caused the Eu-ropean composites production volume to fall significantly in recent years. There has now been another decline in Europe for 2023.
Overall development of the composites market
The volume of the global composites market totalled 13 million tons in 2023. Compared to 2022, with a volume of 12.3 million tons, growth was around 5%. In comparison, the European composites production volume fell by 8% in 2023. The total European composites market thus comprises a volume of 2,559 kilotons (kt) after 2,781 kt in 2022.
The market is therefore declining and falling back to the level of 2014. Overall, market momentum in Europe was lower than in the global market. Europe's share of the global market is now around 20%.
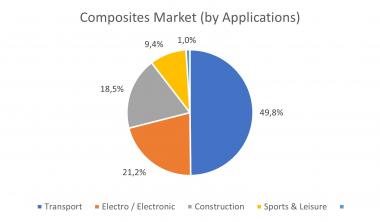
As in previous years, development within Europe is not uniform. The differences are due to very different regional core markets, the high variability of the materi-als used, a wide range of different manufacturing processes and widely differing areas of application. Accordingly, there are different regional trends, especially with regard to the individual processes, although there were declines in all re-gions and for almost all processes in 2023. At almost 50% of the market volume, the transportation sector accounts for the largest share of total composites pro-duction in terms of volume. The next two largest areas are the electri-cal/electronics sector and applications in construction and infrastructure.
The entire market report 2023 is available for download: https://www.avk-tv.de/publications.php.
AVK - Industrievereinigung Verstärkte Kunststoffe e. V. AVK Market report Composites
AVK – Industrievereinigung Verstärkte Kunststoffe e. V.