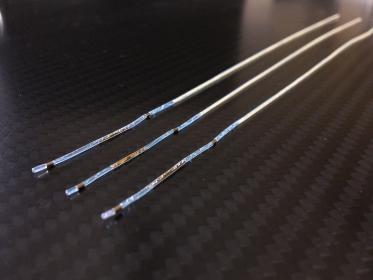
Using textile electrodes to stop muscle tremor
Scientists at the Fraunhofer Institute for Biomedical Engineering IBMT have been working with international partners to develop a technology platform to help relieve the symptoms of muscle tremors. Tiny biocompatible electrodes in the muscles, combined with external electrodes and controllers, form an intelligent network of sensors and actuators to detect muscle signals and provide electrical stimuli as needed. Together with exoskeletons, the technology could also help people with spinal cord injuries.
A compact controller on a belt or under a jacket, a couple of discreet textile electrodes on the arms and legs, and electrodes three centimeters long and barely a millimeter thin in the muscle are all it will take to help people with tremor disorders in the future. Whenever muscle tremors start, the system sends electrical stimuli to the muscles; these stimuli are registered by the nervous system. The nervous system then stops sending interfering signals to the muscles, which settle down again. That is the basic idea behind the technology that scientists from Fraunhofer IBMT have been working on together with project partners by developing, manufacturing, integrating and experimentally testing a set of intramuscular and external electrodes and associated controllers.
The scientists have already made some concrete achievements. “We have managed to reduce muscle tremors significantly in trials with patients,” explains Andreas Schneider-Ickert, project manager for active implants and innovation manager.
The system is part of the EU-funded joint project “EXTEND.” A total of nine project partners from five different countries are working together to develop a versatile platform of distributed neural interfaces. The technology will be able to help people with neuromuscular disorders, such as tremors, or symptoms of paralysis. Even people with spinal cord injuries could benefit from this. The technology uses external controllers to link the implanted electrodes into an intelligent network. The components communicate with each other wirelessly, exchange data, detect muscle signals and send targeted stimuli into the muscles. Implanted systems are already being used medically to provide stimulation, but the current methods require complex surgical operations that are considerably stressful for patients.
Implants for the human-machine interface
A key element of EXTEND is the implants, which are made from biocompatible platinum-iridium and silicone and are injected into the muscle through a catheter. Just three centimeters long and barely a millimeter in diameter, the tiny implant has an electrode at each end that functions as either a sensor or an actuator. External electrodes sewn into a textile ribbon supply the module with energy. This sends pulsed alternating current through the muscle tissue to the implant. “What’s innovative about this is not only the intelligent interplay between control electronics, sensors and actuators, but also the principle of modulating the alternating current to transmit data,” explains Schneider-Ickert.
Once it has been implanted and started, the sensors register the first signs of muscle tremors and pass the information on to the external components. The controller evaluates the data and sends signals through the textile electrodes to stimulate the muscle. This closes a control circuit of intelligently networked sensor and actuator components that counteracts the tremor.
The stimulus signal is not strong enough to trigger a muscle contraction directly. It is the nervous system that plays the decisive role here. This registers the stimulation in the muscle tissue and responds by stopping the commands that trigger the muscle tremor. At least that is the theory — the finer details of the relationship between tremors and signals from the nervous system are yet to be researched. “In clinical trials, however, our method is working astonishingly well. Initial trials have shown that providing the patient with stimuli for one or two hours is enough to reduce tremor symptoms for a longer period of time,” says Schneider-Ickert.
Since tremors often occur in both arms and both legs, implants can be injected and external textile electrodes placed in all the affected muscle groups. This creates a distributed sensor network. The controllers can keep track of all the implanted and external electrodes at the same time and control them in coordination with each other. All this happens in real time, with the person experiencing no delay at all.
The technology being developed in the EXTEND joint project is just as functional as conventional implant systems, but minimally invasive and therefore easier to accept and better for everyday use. The basic concept originates from a Spanish project partner. Based in this concept, the researchers at Fraunhofer IBMT designed the electrodes and implantable components and produced and integrated them in the in-house cleanroom. The scientists have 25 years of expertise in neuroprosthetics and active implants.
Exoskeletons to prevent paraplegia
For tremor patients, EXTEND brings them the hope that their symptoms can be alleviated considerably. However, the technology platform could also help people with spinal cord injuries thanks to motorized exoskeletons. This is a possible because, in cases of paralysis, the nerve fibers are often not completely cut off. They can still transmit stimuli from the brain, albeit very weakly. The sensors register the activity and transmit it to the controller, which analyzes all the signals, works out what movement the person wants to perform and activates exactly the right prostheses to support the muscles in executing the movement.
Following initial successful tests, the concepts and technologies used in EXTEND have been steadily developed, miniaturized, optimized and subjected to further implementation studies. As a result, the project has now been completed with a successful proof of concept of the miniaturized full system in humans. Fraunhofer IBMT will use the knowledge gained from EXTEND to further develop its expertise in the field of neuromuscular and neural interfaces.
Fraunhofer Fraunhofer IMBT textile electrodes Electrodes medical technology EU project
Fraunhofer Institute for Biomedical Engineering IBMT