Bioresorbable membrane: depot for active substances
Fraunhofer researchers have succeeded in using the bioresorbable silica gel Renacer® to produce an electrospun membrane that is neither cytotoxic to cells nor genotoxic. This model mimics fibrous structures found in connective tissue and is therefore particularly suitable for regenerative applications, such as for improved wound healing.
The treatment of large as well as internal wounds is challenging and can be a very lengthy process. Researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute for Silicate Research ISC and the Fraunhofer Institute for Toxicology and Experimental Medicine ITEM have developed a bioresorbable membrane for this use. This membrane supports wound healing and biodegrades completely in the body to a natural substance.
The basis for the novel membrane is a fiber fleece developed at Fraunhofer ISC. This fleece has already been approved as a medical device to support the regeneration of chronic wounds, such as the diabetic foot. During the healing process, the material dissolves completely within six to eight weeks. Using the electrospinning method, the researchers have now managed to reduce the 50-micrometer fiber diameter by a factor of more than 50, resulting in fibers with diameters of less than one micrometer (µm). This made it possible to spin a silica gel sol into an open-meshed silica gel membrane consisting of fibers with a diameter of about one µm. In some cases, the diameters achieved were as small as 100 nanometers. “These fiber systems imitate the extracellular matrix, the fiber structures found in connective tissue, in the body and are very well tolerated by human cells for tissue regeneration. They cause no foreign body reactions and no internal scarring. The innovative silica gel membrane releases only one degradation product, ortho-silicic acid. This has a regenerative effect on the tissue and promotes the closing of wounds,” explains Dr. Bastian Christ, a scientist at the Fraunhofer ISC in Würzburg. Together with his colleagues, he was in charge of the synthesis and processing of the material.
“While the original fiber fleece of 50 µm thick fibers is inserted into a chronic wound from the outside, the thinner fiber fleece is also suitable for internal use. Theoretically, it could be placed onto the filler material used for bone defects in the jaw to accelerate wound healing,” is how Dr. Christina Ziemann, research scientist at Fraunhofer ITEM responsible for the biological evaluation of the material, describes one of numerous possible applications. “In principle, the membrane can be glued in the body with biodegradable adhesives.
Material is neither cyto- nor genotoxic
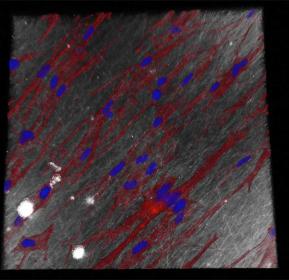
Using a confocal microscope, a special light microscope, it was possible to show that the small-meshed membrane, which serves as a demonstrator, exhibits a barrier function. This prevents the passage of connective tissue cells for a period of at least seven days without interfering with cell proliferation. In addition, the membrane is resorbable, is not cyto- or genotoxic and thus causes no direct damage to tissue or DNA.
Fiber diameter and mesh size influence the behavior of the cells
A thin fiber diameter of 100 nanometers with thin meshes was chosen for use as an adhesion barrier to prevent postoperative adhesions and scarring. With this configuration, only nutrients could pass through the fiber fleece, but connective tissue cells could not. With a fiber diameter of one micrometer and correspondingly wider meshes, on the other hand, the cells grow into the fiber mesh, proliferate there and have a regenerating effect on the surrounding tissue. “By adjusting the material properties, such as fiber diameter and mesh size, it is possible to influence the behavior of the cells as desired,” says Christ. The equipment required for spinning the fibers is designed at Fraunhofer ISC to meet application and specific customer requirements. The shape and size of the fiber fleeces can also be adjusted to customer specifications.
Wounds only heal quickly and effectively if the wounded tissue is sufficiently supplied with nutrients. At the same time, metabolic products have to be removed. In contrast to many products on the market that allow nutrient transport only after biodegradation has started, the open-meshed Renacer® membrane promotes this transport directly after implantation, while not allowing cell passage.
Membrane with an inorganic character
There is another advantage: The Renacer® membrane dissolves completely into almost pH neutral non-toxic ortho-silicic acid, the only water-soluble form of silica. It is physiologically present in the body and has been shown to stimulate connective skin tissue formation and bone formation. Products currently available do not exhibit such bioactive properties. Many biodegradable materials dissolve into organic acids, such as lactic acid or glycolic acid. This can cause local acidification in the tissue, which then triggers inflammatory reactions of the immune system. “Our tests have shown that the dissolution product, ortho-silicic acid, is also non-toxic and completely biocompatible with cells,” says Ziemann. “The membrane decomposes into a single molecule – ortho-silicic acid.”
Fibers as a depot for active substances
Furthermore, drugs can be encapsulated into the matrix of the silica gel fibers, to be released during material resorption. “For example, antibiotics could be delivered into a wound after applying a drug-loaded Renacer® membrane to prevent the formation of bacterial colonies,” elaborates Christ. At Fraunhofer ISC, the BMBF-funded GlioGel project is testing whether the Renacer® material platform can be used as a depot for active substances in the treatment of brain tumors.
Fraunhofer-Institut für Silicatforschung ISC